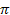 . The sampling distribution of the sample proportion is approximately normal with mean equal to
. The sampling distribution of the sample proportion is approximately normal with mean equal to 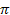 and standard deviation equal to
and standard deviation equal toCentral Limit Theorem (CLT) for Sample Proportion
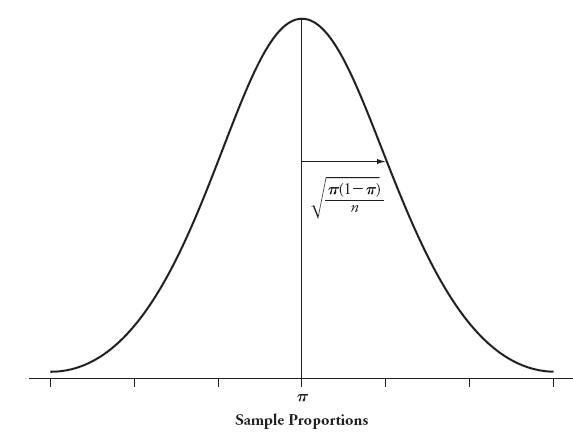
Suppose a simple random sample of size n is to be taken from a large population (more than ten times larger than the sampel size or a process) in which the true proportion (or probability) possessing the attribute of interest is 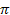 . The sampling distribution of the sample proportion is approximately normal with mean equal to
. The sampling distribution of the sample proportion is approximately normal with mean equal to 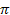 and standard deviation equal to
and standard deviation equal to
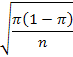
[Note: This normal approximation becomes more and more accurate as the
sample size n increases and is generally considered to be valid as long as
n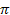 >10 and n(1-
>10 and n(1-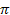 ) > 10.]
) > 10.]